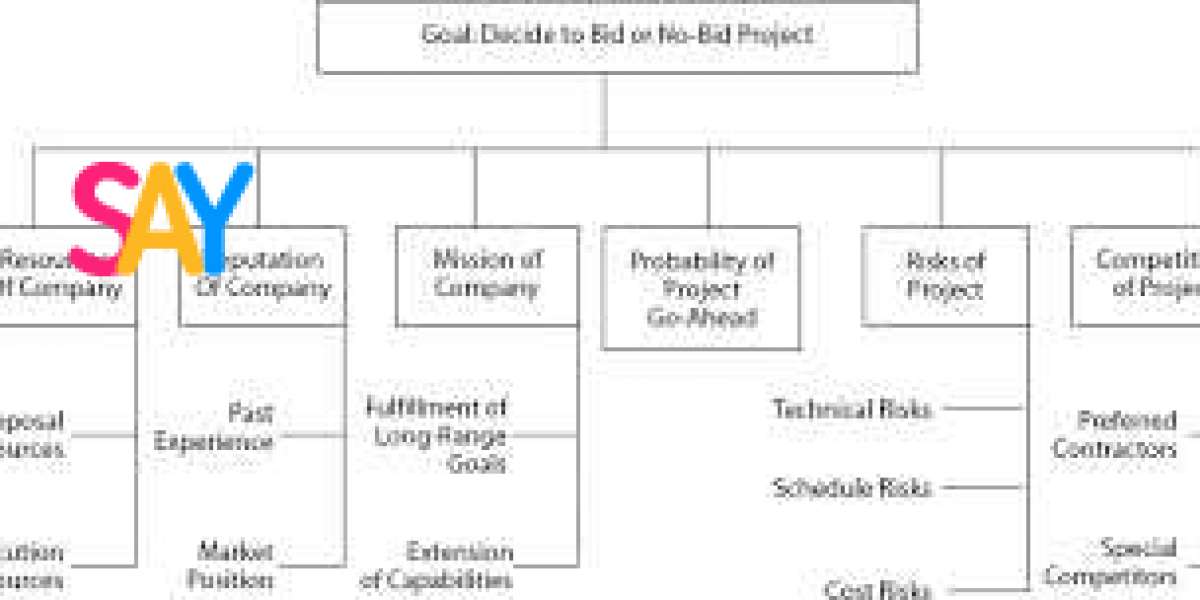
What is Bid-No-Bid Analysis?
Bid-No-Bid Analysis is the process of evaluating a potential opportunity (often in the form of a Request for Proposal, or RFP) to decide whether or not the company should proceed with preparing a proposal. This analysis takes into account a variety of factors, including the alignment with the company’s strategic goals, the competitive landscape, resource availability, potential risks, and the financial upside of the project.
The goal of this process is to avoid wasting resources on bids that have low chances of success or would lead to negative financial or strategic consequences. Instead, it ensures that a company focuses on the opportunities that align best with its capabilities, strengths, and long-term objectives.
Why is Bid-No-Bid Analysis Important?
1. Resource Allocation
Bidding on large contracts is a resource-intensive process. It involves the time, effort, and expertise of various teams—business development, project management, legal, finance, and operations. A Bid-No-Bid Analysis helps to assess whether the potential opportunity justifies the resources required for a competitive bid. This ensures resources are used optimally and not wasted on opportunities with low chances of success.
2. Strategic Alignment
Every organization has its own set of strategic goals and priorities. Not every opportunity will align with these objectives. A Bid-No-Bid Analysis ensures that the decision to bid is based on how well the opportunity fits with the company's vision, capabilities, and long-term growth strategies.
3. Risk Mitigation
Bidding on certain projects, especially those involving new markets or unfamiliar technology, can introduce significant risks. This could range from financial risks due to unfavorable terms to operational risks from handling complex projects. The Bid-No-Bid process helps assess these risks and decide if the potential reward justifies them.
4. Competitive Insight
In highly competitive bidding environments, understanding the competition is crucial. A thorough Bid-No-Bid Analysis provides insights into whether your company can effectively compete against other bidders. It can also highlight whether the project is worth pursuing based on the level of competition and the likelihood of winning the contract.
5. Cost and Profitability Considerations
The financial implications of bidding on a project can be significant. A Bid-No-Bid Analysis takes into account the estimated costs for proposal development, resources needed, and the expected profit margins if the project is won. By assessing whether the potential contract is financially viable, businesses can avoid costly missteps.
Key Factors to Consider in Bid-No-Bid Analysis
A thorough Bid-No-Bid Analysis should take a comprehensive look at various factors that influence the decision-making process. Here are the most important elements to consider:
1. Strategic Fit
- Alignment with Business Goals: Does the opportunity align with your company’s strategic objectives, such as market expansion, new product development, or diversification?
- Core Competencies: Is the project within your company’s area of expertise, or will it require significant investment in new skills or resources?
- Long-Term Value: Will pursuing this opportunity bring long-term value, such as opening doors for future contracts or strengthening relationships with key customers?
2. Financial Considerations
- Profit Margins: What are the expected profit margins for the project? Can your company meet the budgetary expectations without compromising on quality or over-extending resources?
- Bid Costs: What will it cost to prepare the proposal? This includes labor costs, software tools, consultants, travel expenses, and other direct or indirect costs.
- Return on Investment (ROI): What is the potential return on investment from the contract? Does the financial reward justify the effort and resources required to submit the bid?
3. Competitive Landscape
- Market Dynamics: How many competitors are likely to be bidding for the project? Is the opportunity likely to be highly contested, or is there a lack of strong competition?
- Competitive Strength: Does your company have a competitive advantage that makes it more likely to win the bid? Consider your technical expertise, track record, reputation, and past performance in similar contracts.
- Win Probability: What is your company's probability of winning the contract? This can be assessed based on your past win rates, competitor strengths, and the quality of the client relationship.
4. Client Evaluation
- Client Stability and Reputation: Is the client financially stable and reputable? Will winning this contract bring positive publicity, or could there be reputational risks associated with the client or project?
- Relationship with the Client: Does your organization already have a strong relationship with the client, or will this be a completely new engagement? Strong, pre-existing relationships can increase your likelihood of winning the bid.
- Client Expectations and Budget: Are the client’s expectations realistic and within the scope of your capabilities? Does their budget align with your company’s pricing structure?
5. Resource Availability
- Internal Capacity: Does your company have the necessary resources to deliver the project, including the right personnel, technology, and operational capacity?
- Project Complexity: How complex is the project? Will your organization need to bring in external partners or subcontractors to fulfill the requirements, or can it be managed internally?
- Timeline: Do you have the time and resources to meet the client’s deadlines without overextending your team or diverting focus from other critical projects?
6. Risk Assessment
- Legal and Compliance Risks: Are there any legal or regulatory hurdles involved in the project? Will compliance with the contract requirements expose your company to new or unforeseen risks?
- Operational Risks: What are the risks associated with the successful execution of the project? Consider operational complexities, dependencies on third parties, and the potential for cost overruns or delays.
- Economic or Environmental Risks: Are there any external factors, such as economic downturns, political instability, or environmental concerns, that could impact the success of the project?
The Bid-No-Bid Decision Matrix
One effective tool for performing a Bid-No-Bid Analysis is the Bid-No-Bid Decision Matrix. This matrix helps to evaluate the various factors influencing the decision by assigning numerical scores or weightings to different criteria, such as strategic alignment, profitability, resource availability, and competitive positioning. Each factor is assessed based on its importance and impact on the overall decision, allowing decision-makers to make more objective, data-driven conclusions.
For example:
| Factor | Weight | Score (1-5) | Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Fit | 25% | 4 | 1.0 |
| Financial Considerations | 20% | 3 | 0.6 |
| Competitive Landscape | 15% | 2 | 0.3 |
| Client Evaluation | 15% | 5 | 0.75 |
| Resource Availability | 15% | 3 | 0.45 |
| Risk Assessment | 10% | 2 | 0.2 |
| Total Score | 100% | 3.3 |
If the Total Score is above a certain threshold (e.g., 3.5), then the bid is likely worth pursuing. If it is below the threshold, the bid may not be worth the risk and investment.
Best Practices for Effective Bid-No-Bid Analysis
1. Involve Key Stakeholders
Ensure that the decision-making process includes input from all relevant departments—business development, finance, legal, operations, and technical teams. A cross-functional approach will provide a holistic view of the opportunity and help identify any risks or gaps that may not be immediately apparent.
2. Standardize the Process
Develop a consistent, repeatable process for conducting Bid-No-Bid Analysis. This can include the use of decision matrices, checklists, or scoring systems to ensure that each opportunity is evaluated in a structured, thorough manner.
3. Use Historical Data
Leverage historical data from past bids to assess your win rates, typical profit margins, and project complexities. Past performance can help inform future decisions and highlight patterns that might not be obvious on a case-by-case basis.
4. Monitor and Review
Regularly monitor and review your bid decisions to identify areas of improvement. Collect feedback from team members, clients, and other stakeholders to refine your Bid-No-Bid process continuously.
5. Be Ready to Walk Away
Don’t be afraid to walk away from opportunities that don’t align with your company’s strategic goals or pose too much risk. It’s better to decline a bid than to pursue one that could result in a negative outcome for your business.
Conclusion
A Bid-No-Bid Analysis is an essential tool for organizations seeking to optimize their bidding process. By assessing factors like strategic alignment, financial viability, competitive positioning, and resource availability, businesses can make informed decisions about whether or not to pursue a particular opportunity. This strategic decision-making process minimizes wasted