Product design is a multifaceted process that involves the conceptualization, creation, and development of products that meet user needs while being functional, aesthetically pleasing, and economically viable. It combines art, engineering, psychology, and business to deliver products that solve real problems and create value for both customers and businesses. In today’s competitive market, Product Design plays a crucial role in determining the success of a product.
The Importance of Product Design
Product design is more than just aesthetics. While the appearance of a product can influence consumer appeal, great product design is also about usability, functionality, and user experience. A well-designed product addresses the following core areas:
- User needs: Understanding the pain points, desires, and behaviors of the target audience.
- Functionality: Ensuring the product performs its intended purpose effectively and efficiently.
- Aesthetics: Creating an attractive and visually appealing product that aligns with brand identity.
- Economic viability: Designing a product that is cost-effective to produce, distribute, and sell.
- Sustainability: Considering environmental impact and designing with eco-friendly materials and processes when possible.
Successful product design bridges the gap between user needs and business goals, creating products that not only appeal to customers but also align with the company's values and market strategy.
Key Stages of the Product Design Process
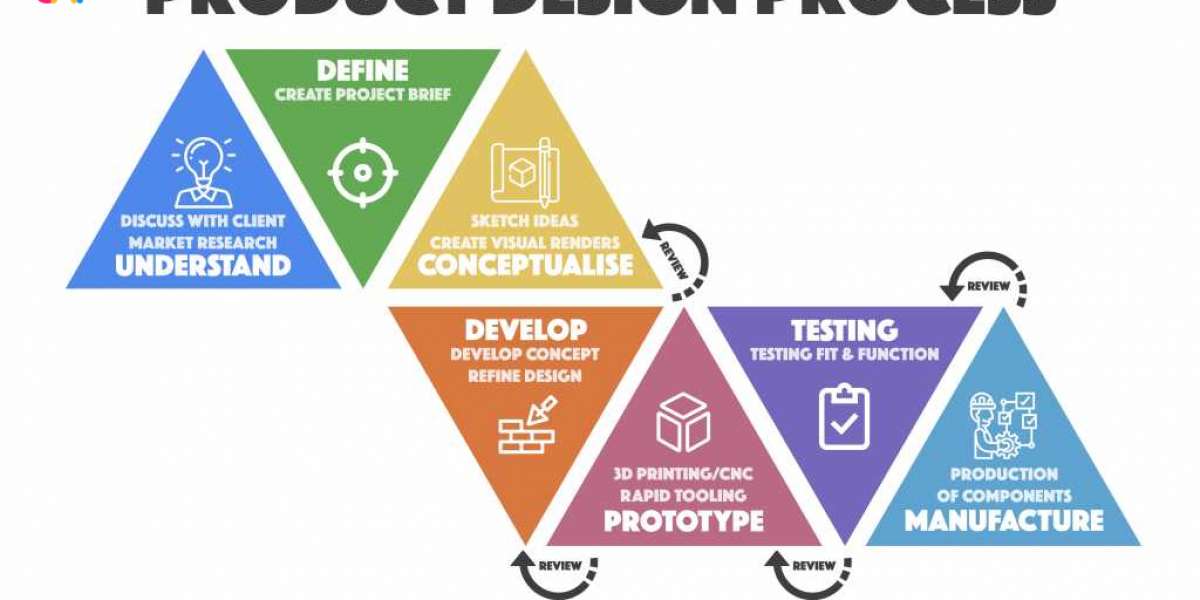
- Research and Discovery The first step in product design is understanding the problem that the product is intended to solve. This involves conducting research on target users, competitors, and market trends. Designers gather qualitative and quantitative data through user interviews, surveys, focus groups, and market analysis. The goal is to uncover insights that inform the design process and ensure that the product aligns with customer needs and expectations.
Key activities include: - Market research
- User research and persona development
- Competitive analysis
- Defining the problem statement
- Ideation and Concept Development Once the problem is clearly understood, the ideation phase begins. This is where designers brainstorm ideas, explore multiple solutions, and think creatively about how to solve the identified problem. Teams often use design thinking techniques such as brainstorming, sketching, and mind mapping to generate a wide range of ideas.
Key activities include: - Brainstorming and idea generation
- Sketching initial concepts
- Creating wireframes or rough prototypes
- Refining ideas based on user needs and feedback
- Prototyping Prototyping is the process of creating a preliminary version of the product to test its functionality, appearance, and user experience. Prototypes can range from low-fidelity paper sketches to high-fidelity digital or physical models. The goal of prototyping is to bring ideas to life and allow designers to explore different iterations of the product before finalizing the design.
Key activities include: - Building low-fidelity (sketches, paper models) or high-fidelity prototypes (3D models, digital mockups)
- Testing functionality, user interaction, and usability
- Gathering feedback from users and stakeholders
- Iterating and refining the design
- Testing and Validation Before a product goes to market, it needs to be thoroughly tested and validated. This stage involves conducting usability testing with real users to identify any issues, pain points, or areas for improvement. Designers collect feedback on how the product performs in real-world scenarios and make necessary adjustments to ensure it meets the needs of its users.
Key activities include: - Conducting usability testing with target users
- Refining the design based on feedback
- Ensuring the product performs as expected in different environments
- Making final adjustments to the design
- Final Design and Manufacturing Once the design is validated through testing, it is finalized for production. This includes creating detailed technical drawings and specifications, selecting materials, and collaborating with engineers and manufacturers to ensure that the product can be produced at scale. The design team works closely with manufacturers to ensure that quality standards are met and that the product is manufactured efficiently and cost-effectively.
Key activities include: - Creating detailed technical specifications
- Selecting appropriate materials and manufacturing processes
- Collaborating with engineers and manufacturers
- Quality control and ensuring design intent is maintained during production
- Launch and Iteration After production, the product is ready to be launched into the market. However, product design doesn’t stop at launch. Designers continue to collect user feedback and monitor how the product performs post-launch. Based on this feedback, iterations and updates may be made to enhance the product’s performance, address any issues, or introduce new features.
Key activities include: - Launching the product in the market
- Gathering post-launch user feedback
- Monitoring product performance and user satisfaction
- Iterating and improving the product as needed
Key Elements of Great Product Design
- User-Centered Design The cornerstone of successful product design is a deep understanding of the user. Designers must put the user at the center of the design process, ensuring that every decision made is informed by user needs, preferences, and behaviors. User-centered design leads to products that are intuitive, easy to use, and aligned with the real-world needs of customers.
- Functionality A beautifully designed product is of little use if it doesn’t function properly. Designers must ensure that the product works as intended, providing a seamless experience for users. This involves attention to detail in ergonomics, user interface (UI), and performance.
- Aesthetics A product’s appearance plays a key role in attracting customers and communicating the brand’s identity. The aesthetic design of a product should be consistent with the values of the brand and appeal to the target audience. Good aesthetics not only make products more appealing but can also enhance usability and user satisfaction.
- Simplicity In product design, simplicity often leads to better user experiences. Overly complex designs can confuse users and create friction. The goal should be to design products that are simple, intuitive, and easy to navigate, reducing cognitive load for the user.
- Sustainability Modern product design increasingly emphasizes sustainability. Designers consider the environmental impact of their choices, from the materials used to the lifecycle of the product. Sustainable design focuses on creating products that are durable, made from eco-friendly materials, and can be recycled or disposed of with minimal environmental harm.
Emerging Trends in Product Design
- Human-Centered AI Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly integrated into product design, particularly in smart devices, software, and services. AI can be used to create more personalized, efficient, and responsive products, but it must be designed with a focus on ethical use and user experience.
- Sustainable Materials As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is growing demand for products made from sustainable, biodegradable, or recycled materials. Designers are responding by exploring innovative, eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes.
- Customization and Personalization Advances in technology, such as 3D printing and modular design, are enabling greater levels of product customization. Consumers now expect products tailored to their individual needs and preferences, from custom-fit apparel to personalized digital interfaces.
- Smart and Connected Devices The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming product design by allowing everyday products to be smart and connected. Designers must now consider how products interact with other devices, integrate into smart ecosystems, and enhance user convenience.
Conclusion
Product Design is a dynamic and evolving field that combines creativity, engineering, and user-centered thinking to create meaningful solutions. It is a process that extends beyond the aesthetic appeal of a product, focusing on functionality, usability, and creating value for both users and businesses. As the market and consumer needs evolve, successful product design will continue to play a critical role in determining which products stand out in a competitive landscape. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and user focus, companies can design products that not only meet market demands but also shape the future of industries.