Gabapentin 400 mg has become an essential drug for the treatment of seizure disorders and peripheral neuropathy, providing patients with these difficult illnesses with respite and an enhanced quality of life. This article explores the effects of gabapentin 400 mg on seizure disorders and peripheral neuropathy. It also covers the drug's mechanism of action, clinical effectiveness, dose recommendations, possible side effects, patient experiences, and future research possibilities. This thorough review attempts to provide insightful information for those in the medical field as well as others who are interested in learning more about the function that gabapentin plays in treating various ailments by looking at the most recent discoveries and research results.
A Synopsis of Gabapentin
The main conditions treated by gabapentin, often marketed under the name Neurontin, are seizures and nerve pain. It's a member of the anticonvulsant medication family and is often recommended for neuropathy, fibromyalgia, and epilepsy.
Gabapentin 400 mg's Significance in Clinical Practice
Because gabapentin 400 mg is so successful at treating seizure disorders and peripheral neuropathy, it is an essential tool in therapeutic practice. For many individuals seeking treatment from these problems, it's a popular option because of its minimal risk of severe side effects and cost.
The Knowledge of Peripheral Neuropathy
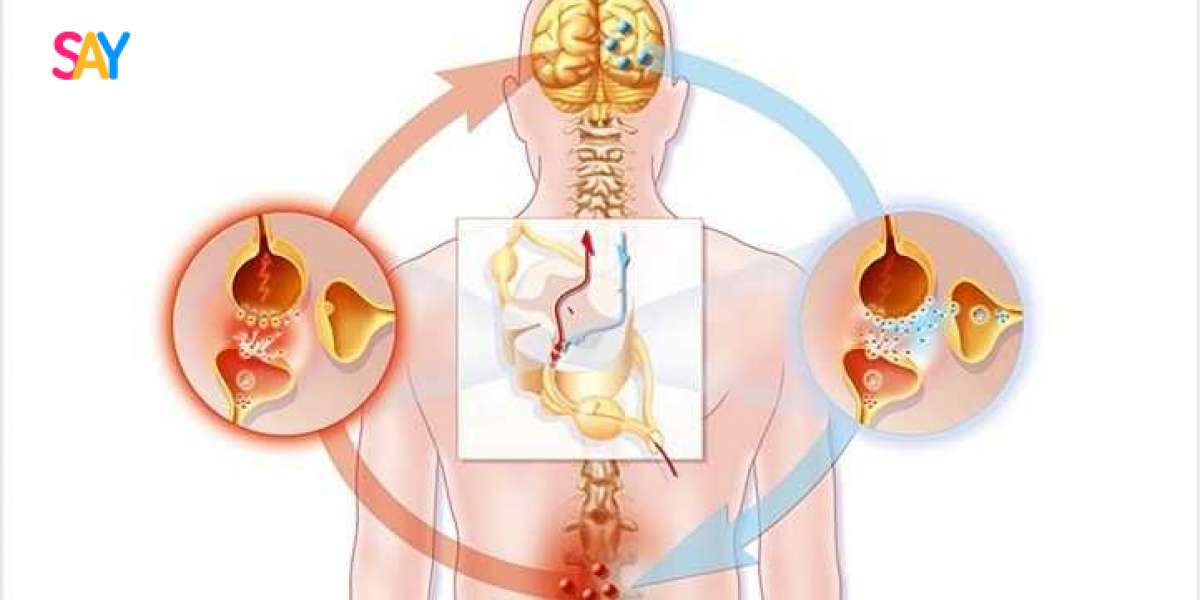
Damage to the peripheral nerves causes a disorder known as peripheral neuropathy, which manifests as tingling, numbness, and pain in the extremities. Numerous conditions, including diabetes, infections, and severe traumas, might be the cause of it.
How the 400 mg of gabapentin Targets Neuropathic Pain
In order to affect how pain is perceived, gabapentin 400 mg modifies the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain and spinal cord. It relieves neuropathic pain linked to diseases like diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia by assisting in the reduction of aberrant electrical activity in injured nerves.
Different Types of Seizures
Epilepsy, another name for seizure disorders, is a general term for a group of neurological diseases marked by abrupt, uncontrollable electrical disruptions in the brain. These seizures might show up as convulsions or as short-lived consciousness lapses.
Gabapentin 400 mg's Function in Controlling Seizures
For the treatment of certain forms of seizures, such as focal and partial seizures, gabapentin 400 mg works well. It works by bringing the brain's electrical activity under control, which lessens the possibility of aberrant impulses that might lead to seizures.
Summary of Important Research on 400 mg Gabapentin
The effectiveness of gabapentin 400 mg in treating peripheral neuropathy and seizure disorders has been shown in several clinical investigations. Its importance in symptom management and enhancing patients' quality of life has been brought to light by these research.
Proof of Gabapentin's Effectiveness
There is substantial evidence to support the effectiveness of gabapentin 400 mg, since many patients report decreased discomfort and seizure frequency after starting medication. The overall study results highlight the usefulness of gabapentin in the management of these difficult situations, even if individual responses may differ.
Suggested Dosage for Neuropathy in the Periphery
The suggested initial dose of Gabapentin 400 mg for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy is usually 300 mg given once day, with progressive titration as required. Up to 600 mg of the dosage may be taken daily in two or three doses. Individual responses, however, could differ, therefore doses have to be customized to meet the unique requirements of each patient.
Guidelines for the Management of Seizures
When gabapentin 400 mg is used to treat seizure disorders, the dose is typically started at 300 mg once day and subsequently increased or decreased according to response and tolerance. Divided into three equal doses, the highest recommended daily dosage for seizure control is 3600 mg. When changing the dose for seizure treatment, it is essential to strictly adhere to a healthcare provider's instructions.
Common Gabapentin 400 mg Side Effects
Symptoms of gabapentin 400 mg often include weariness, sleepiness, dizziness, and problems with coordination. Additionally, gastrointestinal problems including nausea and constipation may strike the patients. It is crucial to keep an eye out for these side effects and to notify a healthcare professional right once if you have any concerns.
Gabapentin 800 mg is used to treat and prevent seizures. It is also used to treat nerve pain in individuals who have had shingles, a painful rash brought on by a herpes zoster virus. Another name for gabapentin is an anticonvulsant or antiepileptic medication.
Particular Attention to Patient Populations
When using gabapentin 400 mg, certain patient populations—such as elderly individuals and those with renal impairment—may need to have their dose adjusted or closely monitored. Furthermore, because of the possibility of abuse, anyone with a history of drug addiction should take this prescription with caution. Women who are expecting or breastfeeding should speak with a doctor before using gabapentin.
First-hand Narratives on the Impact of Gabapentin
Positive experiences with Gabapentin 400 mg have been reported by several people with peripheral neuropathy or seizure disorders, who have seen improvements in seizure control and pain management. With the use of this drug, some people have experienced improved quality of life and greater functional skills.
Effect on Life Quality
Gabapentin 400 mg has helped people with chronic pain from peripheral neuropathy and seizures manage their symptoms, which has improved their quality of life. For many people, everyday tasks have become more doable due to the medication's efficaciousness in managing symptoms.
Overview of the Benefits of Gabapentin 400 mg
In summary, by reducing symptoms and enhancing patient outcomes, gabapentin 400 mg is an important medication for peripheral neuropathy and seizure disorders. For those in need of symptom control, its well-established effectiveness and generally acceptable side effect profile make it a helpful treatment alternative.
Examining Prospective Research Fields to Gain Additional Knowledge
New treatment modalities may be made possible by investigating other uses for gabapentin 400 mg and better comprehending its mechanisms of action as neurology and pharmacology research progresses. Future research in the area might be directed by examining any possible drug interactions and how it affects patient outcomes over the long run.
In summary, the data demonstrate the substantial advantages of gabapentin 400 mg in the efficient treatment of seizure disorders and peripheral neuropathy. Looking forward, further investigation and study of this drug show potential for improving treatment results and the quality of life for others who are coping with similar illnesses. Together, patients and healthcare professionals may overcome these obstacles with more assurance and hope by remaining educated and making the most of Gabapentin 400 mg.