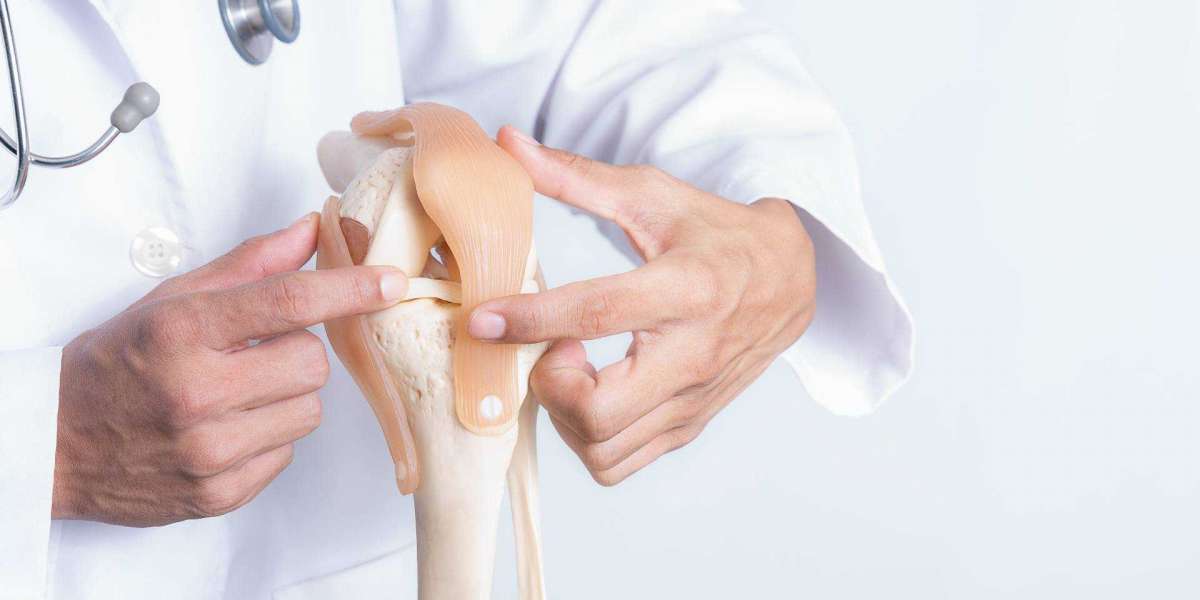
The Fundamentals of Orthopedic Surgery: A Comprehensive Overview
Orthopedic surgery, a specialized field within medicine, focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system. From fractures and joint injuries to degenerative diseases, orthopedic surgeons play a crucial role in restoring mobility, alleviating pain, and improving the overall quality of life for individuals facing musculoskeletal challenges. In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into the basics of orthopedic surgery, unraveling its fundamental principles, key procedures, and the transformative impact it has on patients.
Understanding the Musculoskeletal System
1. The Foundation: Bones and Joints
At the core of orthopedic surgery lies a profound understanding of the musculoskeletal system. Bones provide the structural framework, offering support and protection to vital organs. Joints, where bones meet, facilitate movement and functionality. Orthopedic surgeons navigate this intricate system to diagnose and address a myriad of conditions affecting bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
Gabapentin 100mg is a pharmaceutical formulation belonging to the anticonvulsant class of medications. Primarily recognized for its antiepileptic properties, Gabapentin 100mg also finds utility in the management of certain types of nerve pain. Here is a detailed overview of Gabapentin 100mg.
2. Muscles, Ligaments, and Tendons
Muscles, ligaments, and tendons work in harmony to enable movement and maintain stability. Muscles contract and relax, providing the force needed for motion. Ligaments connect bones to stabilize joints, while tendons connect muscles to bones, transmitting the force generated during movement. Orthopedic surgeons consider the dynamic interplay of these elements in their diagnostic and treatment approaches.
The Core Principles of Orthopedic Surgery
1. Diagnosis: Key to Informed Treatment
Accurate diagnosis forms the cornerstone of orthopedic surgery. Through a combination of patient history, physical examinations, and advanced imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI, orthopedic surgeons pinpoint the source of musculoskeletal issues. Thorough diagnostic assessments guide the formulation of tailored treatment plans.
2. Non-Surgical Approaches: Exhaustive Options
Orthopedic surgeons adopt a conservative approach whenever possible, exploring non-surgical interventions before considering surgery. Physical therapy, medications, lifestyle modifications, and joint injections are among the array of non-surgical options aimed at managing pain and improving function.
Common Orthopedic Procedures
1. Arthroscopy: Precision Through Minimally Invasive Techniques
Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, involves the insertion of a tiny camera (arthroscope) into the joint through small incisions. This allows orthopedic surgeons to visualize and treat a range of joint-related issues, including torn ligaments, damaged cartilage, and inflammation, with precision.
2. Joint Replacement: Restoring Functionality
Joint replacement surgery, particularly for hips and knees, is a transformative orthopedic procedure. It entails replacing damaged joint surfaces with prosthetic implants, alleviating pain, and restoring optimal joint function. This procedure has become a beacon of hope for individuals with severe arthritis or joint degeneration.
Gabapentin 600mg contains the active ingredient gabapentin, which is known for its antiepileptic properties. It modulates the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly inhibiting the abnormal firing of neurons, making it effective in managing seizures.
3. Fracture Repair: Stabilizing Broken Bones
Fracture repair is a fundamental aspect of orthopedic surgery, focusing on realigning and stabilizing broken bones. Surgical techniques may include the use of internal fixation devices such as plates, screws, or rods. These interventions aim to promote proper healing and prevent complications.
4. Spinal Surgery: Addressing Complex Spinal Conditions
Orthopedic surgeons specializing in spinal surgery address a spectrum of spinal disorders, from herniated discs and spinal stenosis to deformities like scoliosis. Surgical interventions may involve decompression procedures, spinal fusion, or the use of implants to stabilize and align the spine.
5. Soft Tissue Repair and Reconstruction: Restoring Stability
Orthopedic surgeons perform soft tissue repair and reconstruction surgeries to address injuries or conditions affecting muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Procedures such as ACL reconstruction or rotator cuff repair aim to restore stability and function to the affected areas.
The Role of Orthopedic Surgery in Trauma
1. Orthopedic Trauma Surgery: Urgent Interventions
Orthopedic surgeons play a critical role in trauma surgery, providing urgent interventions for severe musculoskeletal injuries resulting from accidents, falls, or trauma. These surgeries aim to stabilize fractures, prevent complications, and initiate the healing process promptly.
Technological Advancements in Orthopedic Surgery
1. Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Precision Redefined
Technological advancements, such as robotic-assisted surgery, have revolutionized orthopedic procedures. Robotic systems enhance precision, allowing surgeons to achieve optimal outcomes with smaller incisions, reduced tissue damage, and faster recovery times.
2. Minimally Invasive Techniques: Enhancing Recovery
The ongoing emphasis on minimally invasive techniques is transforming orthopedic surgery. These approaches reduce surgical trauma, minimize scarring, and contribute to quicker postoperative recovery. Patients benefit from shortened hospital stays and faster return to normal activities.
Rehabilitation and Postoperative Care
1. Crucial Phase of Recovery
Rehabilitation is a crucial phase in the orthopedic surgery journey. Postoperative care includes physical therapy, exercises, and lifestyle modifications tailored to the specific surgery and individual needs. Rehabilitation aims to optimize recovery, restore strength, and ensure long-term musculoskeletal health.
The Future Landscape of Orthopedic Surgery
1. Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments
The future of orthopedic surgery is poised to embrace personalized medicine. Tailoring treatments based on an individual's unique anatomy, genetics, and lifestyle factors is expected to optimize surgical outcomes and improve overall patient satisfaction.
2. Research and Innovation: Advancing Care
Ongoing research and innovation in orthopedic surgery continue to shape the future of musculoskeletal care. Clinical trials, collaborative efforts, and advancements in materials and techniques contribute to the evolution of orthopedic surgery, expanding treatment options and enhancing outcomes.
Conclusion: Transforming Lives Through Orthopedic Surgery
In conclusion, orthopedic surgery stands as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with musculoskeletal challenges. From accurate diagnosis to a range of surgical and non-surgical interventions, orthopedic surgeons play a pivotal role in restoring mobility, relieving pain, and improving the overall quality of life for their patients.
As the field continues to evolve with technological advancements and a personalized approach, the future promises even greater precision, efficiency, and transformative impact. Orthopedic surgery remains at the forefront of medical innovation, shaping the landscape of musculoskeletal care for generations to come.