As cannabis legalization continues to spread across the globe, the demand for reliable testing methods grows with it. While cannabis labs use high-end analytical machines like HPLC or GC-MS, not everyone has access to such expensive tools. That’s why THC test kits—specifically those based on Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)—have gained popularity among home growers, small cannabis brands, and curious consumers. These kits offer an affordable, accurate way to evaluate cannabinoid content, particularly THC potency.
But have you ever wondered what goes into making a THC test device? In this article, we’ll go behind the scenes and explore how THC test kits are developed, validated, and refined—turning chemistry into a user-friendly solution for cannabis testing.
1. The Foundation: Cannabinoid Chemistry
The development of any THC potency testing equipment starts with a deep understanding of cannabinoid chemistry. Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, but it’s not the only one of interest. CBD, CBN, CBG, and other cannabinoids must also be distinguishable for accurate profiling.
TLC-based test kits work by separating these cannabinoids on a plate using solvents. Each compound travels a different distance due to its molecular weight and polarity. With the right chemical conditions, these components become visibly distinguishable and quantifiable.
The developers of THC test kits first analyze:
- Molecular weights
- Solubility in different solvents
- Fluorescence or colorimetric response to specific dyes
- Separation potential on silica-coated plates
This stage involves extensive lab testing using known, certified cannabinoid standards to fine-tune how cannabinoids behave under testing conditions.
2. Engineering the THC Test Device
Once the basic science is established, the next phase is hardware development. The average user doesn't want lab-grade complexity, so the goal is to create a kit that simplifies the scientific process without sacrificing accuracy.
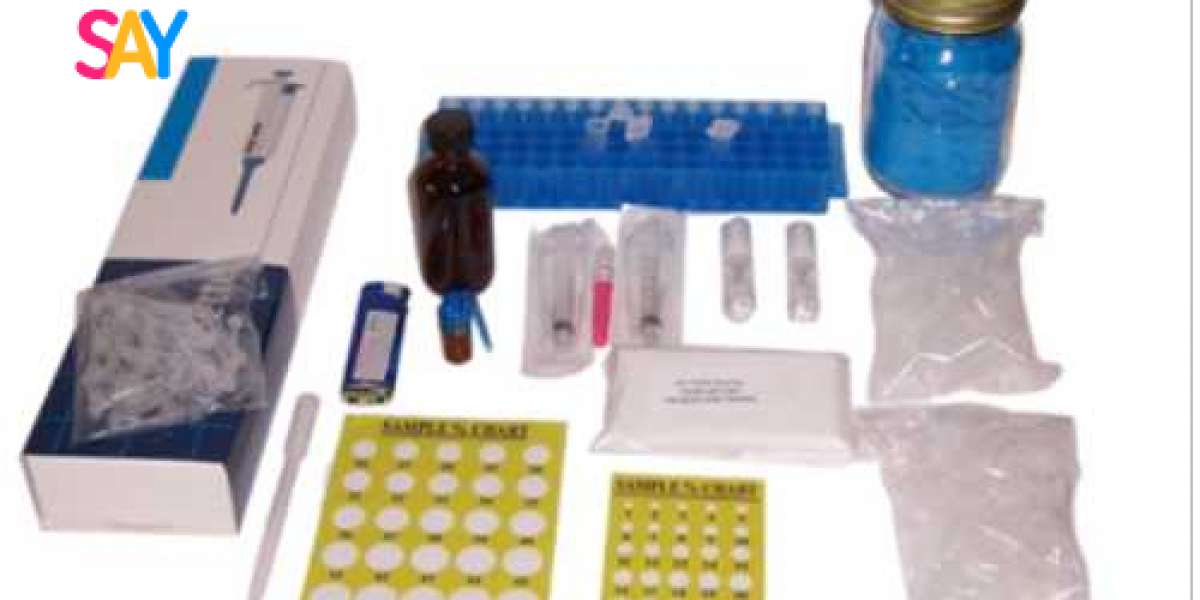
Key components in a THC test device include:
- TLC plates coated with a precise layer of silica gel
- Solvent mixture (also called the mobile phase) that enables cannabinoid separation
- Dye reagent, such as Fast Blue B or other color indicators, that reacts with cannabinoids
- Capillary tubes or pipettes for sample application
- Development chambers, often simple plastic containers
- Reference charts or comparison scales for quantification
Each of these items must be chosen, tested, and calibrated to ensure reproducible results.
3. Trial and Error: Prototype Testing
With a prototype in hand, developers begin iterative testing. This includes:
- Running multiple known cannabinoid samples through the system
- Adjusting solvent concentrations
- Comparing spot development under UV and white light
- Measuring accuracy versus gold-standard equipment like HPLC
If a spot for THC doesn’t consistently appear where it should—or if other cannabinoids show cross-contamination—formulas and techniques are adjusted. The goal is to make the process repeatable and as foolproof as possible for end users.
Developers must also consider:
- Shelf stability of solvents and dye reagents
- Ease of use for non-scientists
- Safety standards for at-home use
- Packaging and durability during shipping
4. Validation Against Lab Results
The gold standard in validating a THC potency testing device is to compare its results with those from a certified analytical laboratory. During this validation phase, kits are tested side-by-side with HPLC or GC-MS machines.
Samples such as flower, oils, and concentrates are tested by both methods to determine:
- Accuracy (how close the TLC results are to the lab values)
- Precision (how consistent results are with repeated trials)
- Range (minimum and maximum cannabinoid concentrations measurable)
- Interference (whether other compounds affect clarity)
Well-designed TLC kits generally report within ±1–2% accuracy when compared to lab equipment, which is more than sufficient for most home and small-batch testing purposes.
5. Creating the Instructional System
Even the best THC test kit is useless if people can’t use it correctly. That’s why a large portion of development focuses on creating easy-to-follow instructions, training videos, and visual comparison charts.
Developers break down the process into simple steps:
- Weigh and prepare the cannabis sample.
- Mix with solvent to extract cannabinoids.
- Spot the solution on a TLC plate.
- Develop the plate in a sealed chamber.
- Apply the dye reagent and let it dry.
- Compare spots to a reference scale to estimate potency.
Educational material often includes tips on testing flower vs. oil, spotting errors, and troubleshooting common issues.
Some manufacturers, like those behind kits at THCTestKits.com, go a step further by offering online video tutorials and one-on-one customer support.
6. Real-World Testing and Feedback
Before release, the kit is distributed to a test group—home growers, cannabis educators, small processors—who put it through real-world use. Their feedback covers:
- Ease of use
- Clarity of instructions
- Accuracy of results
- Problems encountered during testing
This step helps iron out practical issues the lab may not predict—like what happens when a user uses too much sample or doesn’t seal the chamber properly. Once user feedback is incorporated, the kit is finalized for retail.
7. Continuous Improvement and Product Evolution
THC test kits are not static tools. As cannabinoid science evolves, so do testing technologies. New cannabinoids like THCV or CBC may be added. Better solvents and reagents improve detection. Even plate materials might be upgraded for improved resolution.
Reputable kit providers keep their products updated based on new research, legal standards, and user feedback—ensuring that every new batch of THC potency testing equipment is smarter and more precise than the last.
Final Thoughts
The development of a THC test device may seem simple on the surface, but it’s built on layers of science, engineering, validation, and customer-centered design. For small cannabis businesses, home growers, and anyone passionate about quality control, these kits bridge the gap between curiosity and lab-level insight.
Thanks to continued innovation in the field, you don’t need to be a chemist—or spend thousands—to understand your cannabis. All you need is a well-designed test kit, a little patience, and a commitment to transparency.
Explore reliable, lab-inspired THC and CBD test kits at THCTestKits.com and take control of your cannabis knowledge—one test at a time.